What is a Dig in Volleyball?
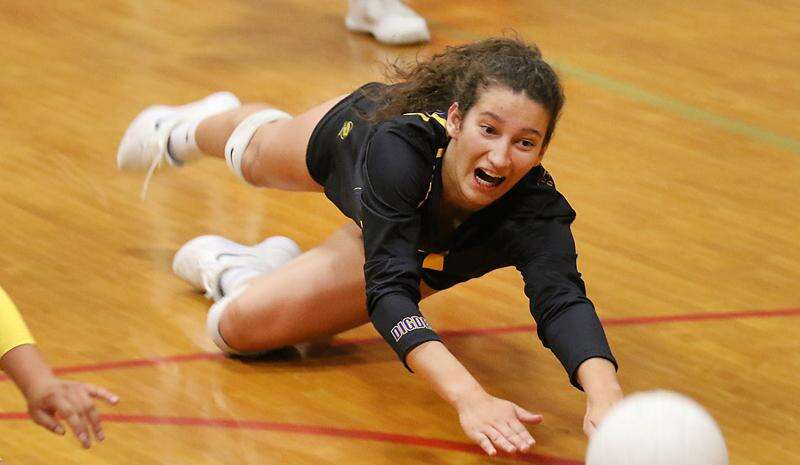
Digs are fundamental defensive moves in volleyball that prevent the ball from touching the ground and preserve a rally by receiving powerful spikes or attacks from the opposing team. By using their hands and arms to create a stable platform, players redirect the ball to their teammates, setting up an opportunity for an effective offensive play. Mastering the dig is essential for any volleyball player as it showcases defensive prowess and seamlessly transitions the game from defence to offence, contributing significantly to a team’s success on the court.
Importance of the Dig in Volleyball Gameplay
The dig is a fundamental aspect of volleyball as it is the foundation for a team’s defensive strategy. With effective offences, opponents’ attacks would result in immediate points, making it easier for teams to gain momentum or stage a comeback. Executing successful digs is vital when facing powerful hitters or performing complex offensive plays.
Additionally, a well-timed dig can smoothly transition the ball from defence to offence, allowing teams to set up an attack quickly. It also showcases the team’s defensive prowess, boosting morale and creating excitement on the court.
What is a Dig in Volleyball?
In volleyball, a “dig” refers to a defensive move where a player receives a powerful attack or spike from the opposing team. A dig is primarily intended to prevent the ball from hitting the ground and to keep the rally alive. Players use their hands and arms to control the ball’s trajectory, directing it upward and towards their teammates, ideally setting up an offensive play. The dig is a crucial defensive skill, allowing the team to transition from defence to offence seamlessly. It requires quick reflexes, precise positioning, and effective communication among teammates. The art of digging plays a vital role in the game’s overall strategy, showcasing a team’s defensive prowess and contributing significantly to its success on the volleyball court.
Digging Technique

The digging technique in volleyball involves a series of coordinated movements and proper form to receive and control the ball effectively during a defensive play. Mastering the digging technique is essential for players to excel in their defensive abilities. Here’s a breakdown of the critical components of the digging technique:
- Ready Stance: The player should maintain a balanced and athletic-ready stance with their knees slightly bent. This position allows for quick reactions and the ability to move swiftly in any direction.
- Anticipation and Reading: Successful digging starts with expectation and reading the opponent’s attack. Players must watch the opposing hitter’s body position and arm swing to predict the direction of the spike.
- Proper Hand Positioning: When the ball is approaching, the player should create a stable platform by holding their arms together with their wrists firmly. The forearms should form a flat surface to absorb the ball’s impact.
- Contact Point: The contact point with the ball should be centred on the forearms, slightly above the wrists. Making clean and controlled contact with the ball is essential to direct its trajectory accurately.
- Body Behind the Ball: Players should align their bodies behind the ball when making contact to achieve better ball control. This helps prevent the ball from deflecting in unintended directions.
- Absorbing the Impact: As the ball makes contact with the forearms, players should slightly bend their elbows and shoulders to absorb the force of the ball, reducing its momentum.
- Directing the Ball: Players need to guide the ball’s trajectory towards the intended target after making contact. The goal is to redirect the ball high enough and accurately towards their teammates, ideally, the setter, to initiate an organized offensive play.
- Recovery: Following the dig, players must be prepared to quickly recover and adjust for the next play. This may involve transitioning into an offensive position or preparing for another potential dig.
- Communication: Effective communication among teammates is vital in defensive play. Players should call out the ball’s location and coordinate with their teammates to avoid confusion and ensure the ball is covered correctly.
- Practice and Repetition: Mastering the digging technique requires consistent practice and repetition. Drills focusing on ball control, footwork, and reading the opponent’s attacks are valuable for improving defensive skills.
By honing their digging technique, volleyball players can become formidable defensive assets, successfully neutralizing opponents’ attacks and keeping their team in control. Physical readiness, mental anticipation, and technical skill are crucial to becoming a proficient digger on the volleyball court.
Common Digging Mistakes

- Incorrect Platform Formation: One of the most common mistakes is failing to form a stable platform with the forearms when attempting a dig. Players might separate their arms too much or have weak wrists, resulting in an unstable surface that makes it difficult to control the ball’s trajectory.
- Late or Early Reactions: Timing is crucial in digging. Players may react too late, causing them to be out of position and unable to reach the ball in time. Conversely, some players might react too early, misjudging the attack’s speed and direction.
- Overreaching: Players may stretch too far to reach the ball, leading to poor ball control and potential mishits. It’s important to move the feet and get in a good position to dig effectively.
- Inadequate Footwork: Footwork is vital in volleyball, and improper movement can hinder effective digging. Players should focus on quick and precise footwork to position themselves correctly and react to the ball’s trajectory.
- Not Keeping Eyes on the Ball: Taking eyes off the ball during an opponent’s attack can lead to misjudging the ball’s flight path and result in missed digs.
- Improper Body Positioning: If players fail to get behind the ball, they might not have enough control to direct it to their teammates accurately.
- Panic Digs: Under pressure, players might resort to panic digs without using proper technique, leading to uncontrolled passes and missed opportunities.
- Lack of Communication: Communication breakdowns can lead to two or more players going for the same ball or no one going for it, leaving the ball undefended.
- Not Adjusting to Serve Receive: Different serving styles require adjustments in the digging technique. Players should adapt their platform and body positioning based on the type of serve received.
- Mental Lapses: Volleyball is a fast-paced game, and mental focus is crucial. Players who lose concentration may react sluggishly or make errors in positioning.
To overcome these mistakes and improve digging skills, players should engage in focused drills that emphasize correct technique, footwork, and communication. They should also work on improving their overall volleyball knowledge and situational awareness to anticipate opponents’ attacks better. Consistent practice, feedback from coaches or teammates, and a willingness to learn from mistakes will help players elevate their digging abilities and contribute significantly to their team’s defensive success.
Defensive Strategies
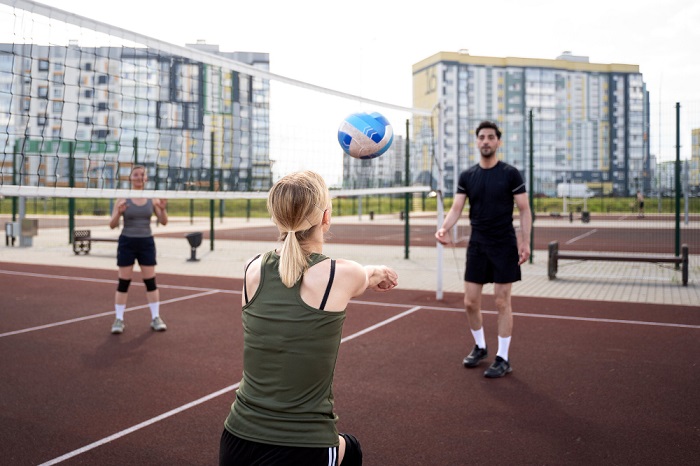

Defensive strategies in volleyball are essential for teams to prevent opponents from scoring and maintain control during rallies. Here are some key defensive strategies employed by teams:
- Blocking: Blocking is a proactive defensive strategy where players at the net attempt to intercept and deflect the ball back into the opponent’s court during an attack. Effective blocking disrupts the opposing team’s offensive plays, forces hitters to adjust their shots, and can lead to point-scoring opportunities.
- Digging: Digging is a reactive defensive strategy used to receive powerful attacks from the opposing team. Players use their hands and forearms to control the ball and prevent it from hitting the floor, keeping the rally alive and allowing for a counterattack.
- Positional Defense: Teams employ positional defense by assigning players specific areas on the court to cover. Each player’s responsibilities are determined based on the opposing team’s tendencies and the hitter’s preferred hitting zones.
- Rotation and Communication: During play, players need to rotate and communicate effectively to ensure the court is adequately covered. Players must call out the ball, communicate defensive shifts, and coordinate seamlessly with teammates to avoid coverage gaps.
- Double Blocking: For particularly strong hitters, teams may employ a double block where two players at the net work together to form a larger blocking wall, making it more challenging for the hitter to find an opening.
- Scouting and Analysis: Teams analyze opponents’ playing styles, offensive patterns, and individual hitter tendencies to develop tailored defensive strategies. Knowing what to expect from the opposing team can enhance defensive preparation.
- Quick Transition: After executing a defensive move, players should quickly transition from defense to offense. This involves moving to the right spots on the court to be ready for the next play and setting up a counterattack.
- Reading the Opponent: Skilled defenders read the opponent’s body language and anticipate their movements to react more effectively during rallies.
- Balancing Defense and Offense: While defense is crucial, teams also need to maintain a balance between defensive focus and offensive opportunities. A successful defensive play should lead to a well-organized offensive response.
- Adjusting Strategies: As the game progresses, teams must be adaptable and make adjustments to their defensive strategies based on the opponent’s performance and the evolving dynamics of the match.
Implementing these defensive strategies requires teamwork, communication, and individual skill. A strong defense can make a significant difference in volleyball matches, helping teams stay competitive, turn rallies in their favor, and ultimately achieve victory.
Advanced Digging Techniques

Advanced digging techniques in volleyball go beyond the basic fundamentals and are employed by skilled players to handle challenging defensive situations. These techniques require exceptional reflexes, athleticism, and a deep understanding of the game. Here are some advanced digging techniques:
- Dive and Roll: In situations where the ball is out of reach for a standard dig, players can perform a dive and roll technique. This involves diving towards the ball, making a controlled contact with the forearms, and rolling out of the landing to minimize impact and maintain control.
- Overhead Dig: Also known as a “sky ball” or “pancake,” the overhead dig is used when the ball is very close to the floor. Players lay their hand flat on the ground, using an open palm to direct the ball upwards. This technique requires quick reflexes and precise timing.
- Defensive Jumps: Skilled defenders can time their jumps to block hard-driven balls directed at them. By jumping slightly before the hitter contacts the ball, they can use their fingers to redirect the ball back into their own court for a better dig opportunity.
- Contact with Fingertips: For balls that are coming in at high velocity, advanced players may use their fingertips to absorb the impact, providing better control over the ball’s trajectory.
- Backcourt Defense (Libero): The libero, a specialized defensive player, excels in backcourt defense, covering a vast portion of the court and making challenging digs. Their exceptional passing skills and reading of the game contribute significantly to their team’s defensive success.
- Utilizing the Block: Players can use the block to assist in digging by positioning themselves near the block to receive deflected balls. This technique requires coordination and communication with the blockers.
- Recovery Digs: After a successful block or a teammate’s block attempt, the ball may rebound in unexpected directions. Advanced defenders anticipate these situations and quickly adjust to make recovery digs, ensuring the ball stays in play.
- Off-the-Net Digs: When an opposing hitter executes a tight net shot, advanced players can adapt their digging technique by angling their platform to keep the ball from contacting the net and landing on their side of the court.
- Reading Spin and Direction: Expert defenders can discern the spin and trajectory of the ball based on the hitter’s arm swing, allowing them to position themselves more effectively and increase their chances of a successful dig.
- Covering Tips and Off-Speed Hits: Advanced defenders are quick to react to tips and off-speed hits, moving swiftly to cover these softer shots and prevent them from falling for easy points.
These advanced digging techniques require extensive practice and experience. Mastering them enables players to handle a wider range of defensive situations and contribute significantly to their team’s success on the volleyball court.
Digging in Different Playing Conditions
Digging in volleyball can vary significantly based on the playing conditions, such as the type of court surface (indoor vs. beach volleyball) and external factors like weather conditions. Players must adapt their defensive strategies and techniques accordingly. Here’s how digging differs in different playing conditions:
Indoor Volleyball:
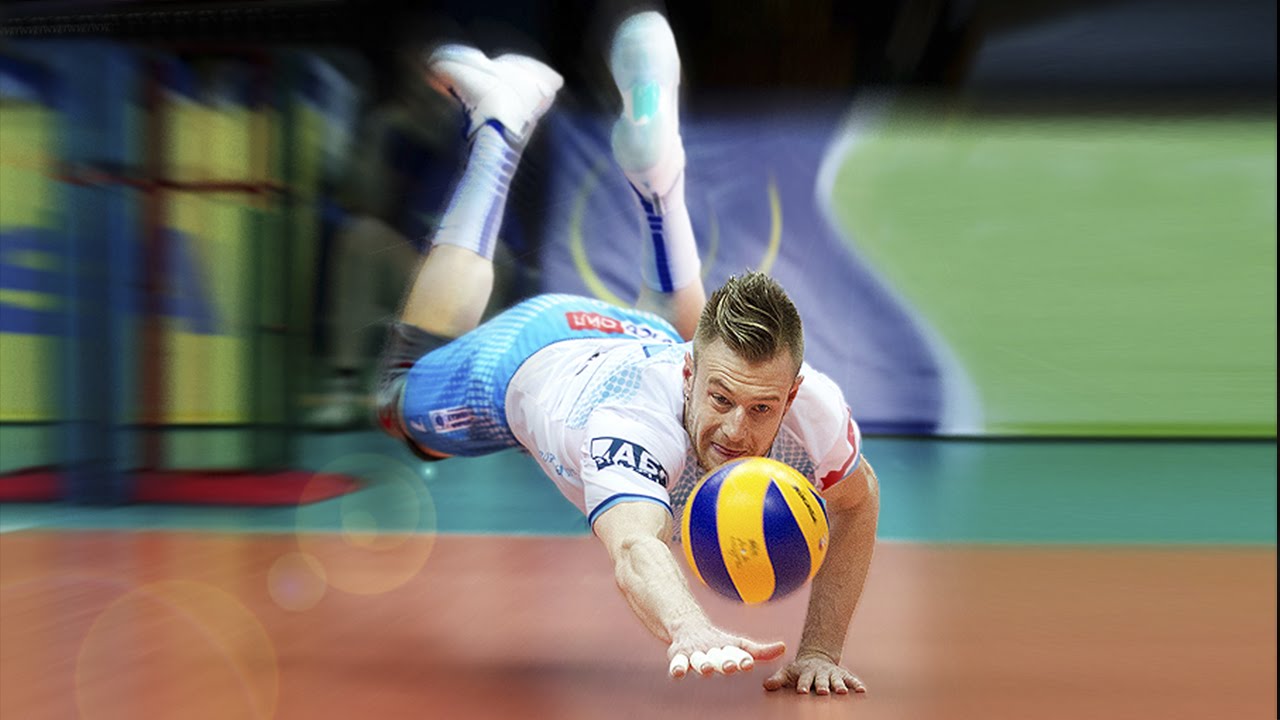

- Hard Court Surface: Indoor volleyball is typically played on a hard court surface, which offers consistent and predictable ball bounces. Players can rely on their footwork and positioning to anticipate the ball’s trajectory during digs.
- Lighting and Ceiling Height: Indoor volleyball courts have controlled lighting, which ensures clear visibility. However, players need to be aware of the ceiling height, especially during powerful attacks, to avoid potential ball interactions with the ceiling.
- Team Defense: In indoor volleyball, team defense is crucial, and players must communicate effectively to cover all areas of the court. Precise digging and passing are essential to maintain offensive plays and set up successful attacks.
Beach Volleyball:
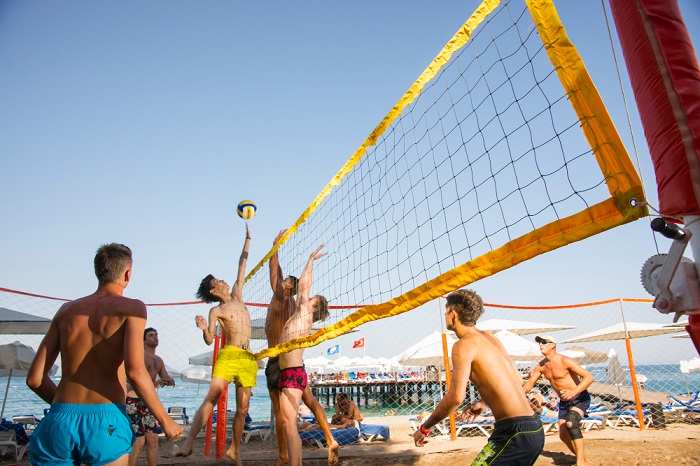

- Sand Surface: Beach volleyball is played on sand, which makes digging more challenging due to the softer and less predictable nature of the surface. Players must adjust their footwork and balance to move efficiently in the sand.
- Wind and Weather: Wind is a significant factor in beach volleyball, affecting the ball’s flight path and making it harder to predict. Players must adjust their defensive positioning and timing to account for wind conditions.
- Individual Defense: In beach volleyball, individual defense plays a more prominent role as players are responsible for covering a larger portion of the court. Players need to be versatile and adept at making digs from various angles.
- Sun Glare: Sun glare can be an issue for players on one side of the court during certain times of the day. Adjusting body positioning and using appropriate eye protection can help players deal with this challenge.
- Surface Variations: Sand surfaces can vary from one beach to another, affecting how the ball behaves during digs. Players must adapt quickly to these surface differences.
Adapting to Both Conditions:
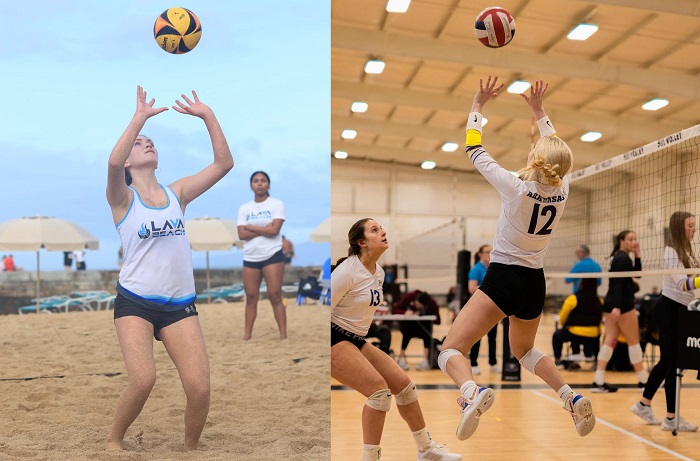

- Footwork and Balance: Regardless of the playing condition, footwork and balance are crucial for effective digging. Players must stay light on their feet and maintain stability to react quickly to the ball.
- Reading Opponent’s Hits: Being able to read the opponent’s hitting style is essential in both indoor and beach volleyball. Anticipating the direction and speed of the ball helps defenders position themselves for successful digs.
- Communication: Effective communication among teammates is vital in both indoor and beach volleyball. Players must call out the ball, communicate defensive shifts, and coordinate seamlessly to avoid coverage gaps.
Digging Tips from Professional Players

Tips from professional volleyball players can offer valuable insights and guidance to aspiring defenders looking to improve their digging skills. Here are some key digging tips from seasoned athletes:
- Stay Low and Ready: Professional players emphasize the importance of maintaining a low and ready stance. Being prepared with bent knees and an alert posture allows for quicker reactions to incoming attacks.
- Anticipate and Read the Hitter: Top players stress the need to study opponents’ hitting tendencies and body language. Anticipating the direction and power of the attack helps defenders position themselves for successful digs.
- Focus on Footwork: Footwork is crucial in effective digging. Professionals recommend constantly moving and adjusting foot positioning to be in the right place at the right time.
- Improve Ball Control: Developing strong forearm passing skills is essential. Professionals emphasize the importance of creating a stable platform with the forearms and wrists to control the ball’s trajectory accurately.
- Keep Eyes on the Ball: Maintaining visual contact with the ball throughout the rally is critical. Professionals advise against taking eyes off the ball to avoid misjudging its flight path.
- Practice Different Digging Techniques: Learning various digging techniques, such as diving and rolling, can be advantageous in making difficult digs when standard techniques may not suffice.
- Adapt to Playing Conditions: Professionals stress the need to adapt to different playing conditions, including court surfaces, lighting, and weather elements. Being flexible and adjusting quickly is vital in top-level competition.
- Work on Defensive Mindset: A strong defensive mindset is crucial in digging. Professionals emphasize the importance of staying mentally focused, positive, and resilient throughout the match.
- Learn from Experience: Professionals advise young players to learn from every digging attempt, whether successful or not. Each experience provides an opportunity for improvement.
- Consistent Practice: Regular and dedicated practice is key to becoming a proficient digger. Professionals stress the significance of repetition and continuous improvement in defensive skills.
- Fitness and Conditioning: Being in top physical condition is essential for successful digging. Professionals emphasize the importance of fitness and agility training to enhance defensive performance.
- Teamwork and Communication: Defenders should communicate effectively with teammates to avoid overlapping responsibilities and ensure full court coverage during digs.
By incorporating these tips into their training and gameplay, aspiring volleyball players can elevate their defensive skills and develop into more well-rounded and effective diggers. Learning from the experiences of professional players can provide valuable insights and inspiration for achieving excellence in the art of digging.
FAQ
What is a dig in volleyball?
A dig in volleyball refers to a defensive move where a player receives a powerful attack or spike from the opposing team. The primary objective is to prevent the ball from hitting the floor and keep the rally alive, allowing for a counterattack.
Why is the dig important in volleyball?
The dig is crucial in volleyball as it is the first line of defense against powerful attacks. It keeps the ball in play and transitions the game from defense to offense, setting up scoring opportunities for the team.
What body part is used to execute a dig?
Players typically use their forearms to create a stable platform for digging. The forearms form a flat surface to control the ball’s trajectory and direct it towards their teammates.
Are there different types of digs in volleyball?
Yes, there are different types of digs in volleyball, including the standard forearm dig, overhead dig (pancake), back-row dig, roll dig, and dive dig. Each type is used based on the ball’s height, speed, and direction.
Who usually performs the dig in a volleyball team?
Digging is a skill required of all players, but back-row defenders and the specialized defensive player called the libero typically handle most of the digging responsibilities.
What happens after a successful dig?
After a successful dig, the team transitions to offense. The ball is passed to the setter, who sets up an attacking play, allowing hitters to attempt a spike and score points.
Can a dig be used in beach volleyball too?
Yes, digging is an essential skill in beach volleyball as well. Players use similar techniques but must adjust to the softer sand surface and different weather conditions.
How can I improve my digging skills?
To improve digging skills, focus on footwork, positioning, and reading the opponent’s attacks. Consistent practice, drills, and playing in game-like situations will help enhance your defensive abilities.
What are some common mistakes in digging, and how can I avoid them?
Common digging mistakes include incorrect platform formation, late reactions, overreaching, and lack of communication. Focus on technique, footwork, and staying mentally engaged to avoid these errors.
What role does communication play in successful digging?
Communication is crucial in successful digging. Players need to call out the ball, coordinate defensive shifts, and work as a team to cover the court effectively and prevent defensive gaps.
Volleyball Related Questions

I’m James Ritter, a sports enthusiast. I’ve played sports since school, and now I enjoy writing about them. My goal is to inspire aspiring athletes through stories of success and determination. I believe anyone can achieve greatness with the right guidance. I aim to make a positive impact on the sports community by sharing stories and insights, connecting my love for sports and writing. Join me on this journey of inspiration for all sports lovers.






